SCIENCE CH-1 MATTER IN OUR SURROUNDING
CHAPTER -- 1
MATTER IN OUR SURROUNDING
TOPICS TO BE COVERED
1. MATTER
2. CHARACTERSTIC OF MATTER
3. DIFFUSION
4. STATE OF MATTER
5. CHANGE OF STATE OF MATTER
6. PHYSICAL STATE OF WATER
7. EVAPORATION
8. FACTORS AFFECT EVAPORATION
1. MATTER
ANYTHING THAT HAVE MASS AND OCCUPY SPACE IS CONSIDERED AS MATTER.
FOR EG WOOD , STONE , GLASS
2. CHARACTERSTIC OF MATTER
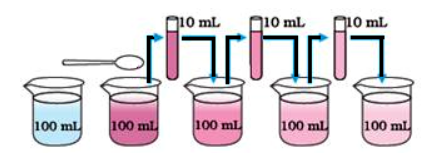
1.PARTICLE OF MATTER ARE VERY SMALL
EG. IF WE TAKE TWO CRYSTAL OF POTTASIUM PHERMAGNET AND DISSOLVE IT IN 100 ML OF WATER. THE WATER GET PURPLE IF WE TAKE OUT 10 ML OF WATER FROM IT AND MIX IT IN ANOTHER 100 ML OF WATER U WILL NOTICE IT WILL GET THE COLOR.
--THIS IS BECAUSE THE PARTICLE OF MATTER ARE VERY SMALL
2. PARTICLE OF MATTER ARE COUNTINUESLY MOVING
EG. IF WE BURN AN INSANE STICK( AGARBATTI) IT SMELL WILL BE SPREAD TILL LONG DISTANCE . THIS IS BECAUSE THE PARTICLE ARE CONTINUESLY MOVING IN THE AIR AND GETTING DIFFUSED WITH THE OTHER PARTICLES IN AIR

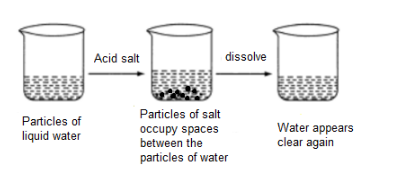
3. PARTICLE OF MATTER HAVE SPACES BETWEEN THEM
EG. WE HAVE SEEN IN UPPER EXAMPLES THAT THE PARTICLES OF MATTER ARE MIXING IN EACH OTHER. THIS IS POSSIBLE BECAUSE THE PARTICLE OF MATTER HAVE SPACES BETWEEN THEN . SO THE OTHER PARTICLE CAN BE DIFFUSED.
4. PARTICLE OF MATTER ATTRACT EACH OTHER
EG. IF WE TAKE A EXAMPLE OF A ROCK , WE WILL SE THAT IT NOT BREAK EASILY AS THEIR PARTICLE FORCE OF ATTRACTION IS VERY HIGH
EG. IF WE TAKE A EXAMPLE OF A CHALK IT WILL BREAK EASILY AS IT PARTICLE FORCE OF ATTRACTION IS LESS

3.DIFFUSION
THE INTERMIXING OF PARTICLE OF MATTER FROM LOWER CONCENTRATION TO HIGHER CONCENTRATION IN AIR .

EG. THE PARTICLE OF DYE MOLECULE IS MIXING WITH THE PARTICLE OF WATER MOLECULE FROM LOWER TO HIGHER CONCENTRATION .
States of Matter
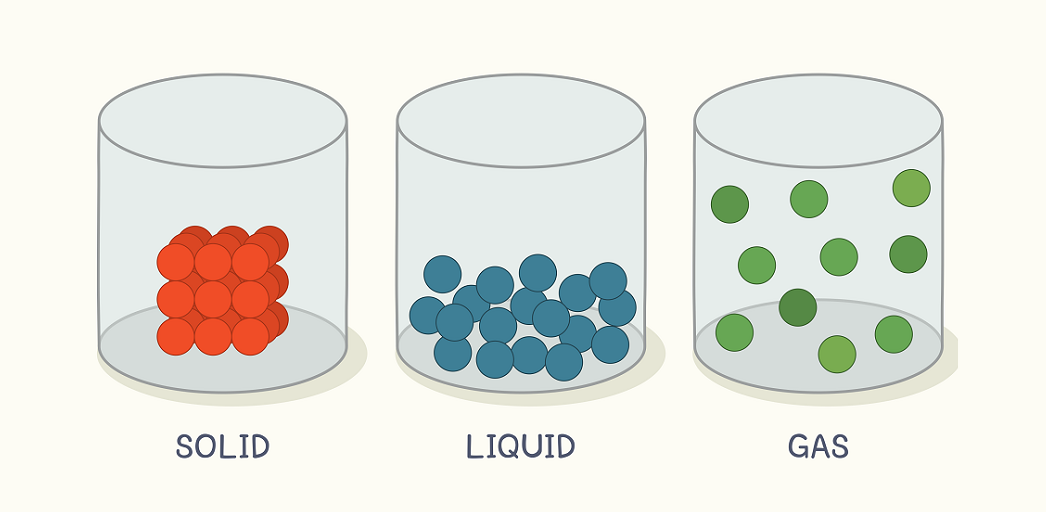
Now we know that particles of matter have a force of attraction between them. Based on this criterion, we can say that matter is present in three different states: solid state, liquid state, and gaseous state.
The Solid State
1. Solids are the objects that have these three properties:
- They have a specific shape.
- They have distinct boundaries.
- They have a volume.
No comments